Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ohira, Saki; Abe, Takeyasu; Iida, Yoshihisa
Radiochimica Acta, 111(7), p.525 - 531, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)The solubility of  Nb in calcium alkaline solutions is one of the important parameters in safety assessment of intermediate-depth disposal which are assumed to use cementitious materials. Nb solubility and solubility-limiting solid phases of Nb in these systems remain unclear. The oversaturation solubility experiments were performed systematically in the 0.001-0.1 M CaCl
Nb in calcium alkaline solutions is one of the important parameters in safety assessment of intermediate-depth disposal which are assumed to use cementitious materials. Nb solubility and solubility-limiting solid phases of Nb in these systems remain unclear. The oversaturation solubility experiments were performed systematically in the 0.001-0.1 M CaCl solutions under alkali conditions, and the characterization of precipitated solid phase controlling Nb solubility was conducted. The negative dependence of Nb solubilities on pH and Ca concentration was observed in solubility experiments, the molar ratio of Nb to Ca of precipitated solid phase was 0.66. The pH and Ca dependence of Nb solubilities was reproduced by the reaction with Nb aqueous species Nb(OH)
solutions under alkali conditions, and the characterization of precipitated solid phase controlling Nb solubility was conducted. The negative dependence of Nb solubilities on pH and Ca concentration was observed in solubility experiments, the molar ratio of Nb to Ca of precipitated solid phase was 0.66. The pH and Ca dependence of Nb solubilities was reproduced by the reaction with Nb aqueous species Nb(OH)
 and Ca-Nb oxide with the molar ratio of Nb to Ca 0.66, e.g., Ca
and Ca-Nb oxide with the molar ratio of Nb to Ca 0.66, e.g., Ca Nb
Nb O
O (am).
(am).
Kobayashi, Taishi*; Nakajima, Shogo*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Matsumura, Daiju; Saito, Takumi*; Sasaki, Takayuki*
Langmuir, 35(24), p.7995 - 8006, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:22.5(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Sakamoto, Yoshifumi; Iida, Yoshihisa; Negishi, Kumi; Taki, Hiroshi; Akai, Masanobu; Jinno, Fumika; Kimura, Yuichiro; Ueda, Masato; Tanaka, Tadao; et al.
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Minase, Naofumi; Iida, Yoshihisa; Tanaka, Tadao; Nakayama, Shinichi
JAERI-Conf 2005-007, p.150 - 155, 2005/08
no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Negishi, Kumi; Ebashi, Katsuhiro; Inagaki, Shingo*; Shibata, Mitsunobu*; Tanaka, Tadao; Nakayama, Shinichi
JAERI-Conf 2004-011, p.139 - 140, 2004/07
Uncertainties should be quantitatively assessed in a long-term assessment of radioactive waste disposal. We focus our experimental efforts on parameters that induce major uncertainties in the radionuclide migration analysis and that have not been quantitatively understood. Solubility of radionuclides, diffusion in bentonite buffer material and sorption on rocks were investigated to quantify the uncertainties associated with the parameters and to minimize the uncertainties.
Kato, Hiroshige*; Mine, Tatsuya*; Mihara, Morihiro; Oi, Takao; Honda, Akira
JNC TN8400 2001-029, 63 Pages, 2002/01
Cementitious materials will be used for the TRU waste repository as a component of engineered barrier system. The distribution coefficients which represent the retardation of radionuclides migration for the cementitious materials would be one of the important parameter for the safety assessment. The much information of radionuclide sorption onto the cementitious materials has been accumulated through the study in the world. Therefore it is necessary to compile the information and Kd of the radionuclides reported in previous studies. In this report, the Kd of the important radionuclides, such as C, Ni, Se, Sr, Zr, Nb, Mo, Tc, Sn, I, Cs, Sm, Pb, Ra, Ac, Th, Pa, U, Np, Pu, Am, Cm, for the cementitious materials were compiled as the Sorption Database (SDB). For radionuclides to be sensitive to the redox potential, e.g. Se, Tc, Pa, U, Pu and Np, some Kds measured under the controlled atmosphere had been reported, and few Kds measured under the controlled redox potential had been reported. For Se, Mo, Sm, Cm and Ac, the distribution coefficients had not been reported, therefore distribution coefficients of Se and Mo for OPC (Ordinary Portland Cement) pastes were measured by batch sorption experiments and these data were added into the SDB.
 /supercritical CO
/supercritical CO +TBP system
+TBP systemMeguro, Yoshihiro; Iso, Shuichi; Yoshida, Zenko
Proceedings of International Solvent Extraction Conference 2002 (CD-ROM), p.1131 - 1136, 2002/00
no abstracts in English
Iida, Yoshihisa; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Nakayama, Shinichi; *; Sakamoto, Yoshiaki
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.663, p.1143 - 1149, 2001/00
no abstracts in English
 to obtain the high U solution
to obtain the high U solution; *; Sakurai, Koji*; ; Nomura, Kazunori; *
JNC TN8400 2000-032, 98 Pages, 2000/12
Concerning the preparation of high U solution for the crystallization process and the application of UO powder dissolution to that, the effects of final U concentration, dissolution temperature, nitric acid concentration and powder size on the dissolution of UO
powder dissolution to that, the effects of final U concentration, dissolution temperature, nitric acid concentration and powder size on the dissolution of UO powder in the nitric acid where the final U concentration was
powder in the nitric acid where the final U concentration was  800g/L were investigated. The experimental results showed that the solubility of UO
800g/L were investigated. The experimental results showed that the solubility of UO decreased with the increase of final UO
decreased with the increase of final UO concentration and powder size, and with the decrease of dissolution temperature and nitric acid concentration. It was also confirmed that in the condition where the final U concentration was sufficiently lower than the solubility of U, UO
concentration and powder size, and with the decrease of dissolution temperature and nitric acid concentration. It was also confirmed that in the condition where the final U concentration was sufficiently lower than the solubility of U, UO dissolution behavior in the high U solution could be estimated with the equation based on the fragmentation model which we had already reported. Based on these experimental results, the dissolution behavior of irradiated MOX fuel in high U solution was estimated and the possibility of supplying high U solution to the crystallization process was discussed. In the preparation of high U solution for the crystallization process, it was estimated that the present dissolution process (dissolution for fuel pieces of about 3cm long) needed a lot of time to obtain a high dissolution yield, but it was shorted drastically by the pulverization of fuel pieces. The burst of off-gas at the early in the dissolution of fuel powder seems to be avoidable with setting the appropriate dissolution condition, and it is important to optimize the dissolution condition with considering the capacity of off-gas treatment process.
dissolution behavior in the high U solution could be estimated with the equation based on the fragmentation model which we had already reported. Based on these experimental results, the dissolution behavior of irradiated MOX fuel in high U solution was estimated and the possibility of supplying high U solution to the crystallization process was discussed. In the preparation of high U solution for the crystallization process, it was estimated that the present dissolution process (dissolution for fuel pieces of about 3cm long) needed a lot of time to obtain a high dissolution yield, but it was shorted drastically by the pulverization of fuel pieces. The burst of off-gas at the early in the dissolution of fuel powder seems to be avoidable with setting the appropriate dissolution condition, and it is important to optimize the dissolution condition with considering the capacity of off-gas treatment process.
Kobayashi, Kaoru*; Kaminaga, Masanori; Haga, Katsuhiro; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Aso, Tomokazu; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Hino, Ryutaro
JAERI-Data/Code 2000-037, 69 Pages, 2000/12
no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji
JAERI-Data/Code 2000-031, 131 Pages, 2000/11
no abstracts in English
; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*; Kagawa, Akio;
JNC TN8400 2000-017, 30 Pages, 2000/03
The influence of the cement additives on the distribution coefficients of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite was confirmed. The adsorption experiment of americium-241 to Ca-bentonite with cement additives was performed by the batch method, as a part of the influence evaluation of the organic in the research of TRU waste disposal. As a result, the distribution coefficient of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite was over 1.2E+3m /kg in the condition of the absence of cement additives. In the case of low concentration (0.3g/kg) of the naphthalenesulfonic acid type cement additives, the distribution coefficient was 5.2E+2m
/kg in the condition of the absence of cement additives. In the case of low concentration (0.3g/kg) of the naphthalenesulfonic acid type cement additives, the distribution coefficient was 5.2E+2m kg. And, in the case of high concentration (30g/kg) of the same cement additives, the distribution coefficients was 2.0E-1m
kg. And, in the case of high concentration (30g/kg) of the same cement additives, the distribution coefficients was 2.0E-1m /kg. On the other hand in the case of flow concentration (0.5g/kg) of the polycarboxylic acid type cement additives, the distribution coefficients was over 1.3E+3m
/kg. On the other hand in the case of flow concentration (0.5g/kg) of the polycarboxylic acid type cement additives, the distribution coefficients was over 1.3E+3m /kg. And, in the case of high concentration (50g/kg) of the same cement additives, the distribution coefficient was 1.8E-1m
/kg. And, in the case of high concentration (50g/kg) of the same cement additives, the distribution coefficient was 1.8E-1m /kg. Here, selected cement additives concentrations were based on a standard concentration of 10g/kg when the ratio of water:cement is about one. From these results, the distribution coefficient of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite decreases according cement additive concentration. The distribution coefficients were similar on different kinds of cement additives. The cement additives concentration influences the distribution coefficient. The distribution coefficient was small in the case of high concentration of the cement additives. That is, it is thought that the cement additives have small influences on the distribution coefficient of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite in the case of low concentration, though the cement additives have influences on the distribution coefficient of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite in the case of high concentration.
/kg. Here, selected cement additives concentrations were based on a standard concentration of 10g/kg when the ratio of water:cement is about one. From these results, the distribution coefficient of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite decreases according cement additive concentration. The distribution coefficients were similar on different kinds of cement additives. The cement additives concentration influences the distribution coefficient. The distribution coefficient was small in the case of high concentration of the cement additives. That is, it is thought that the cement additives have small influences on the distribution coefficient of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite in the case of low concentration, though the cement additives have influences on the distribution coefficient of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite in the case of high concentration.
; Koyama, Tomozo; Funasaka, Hideyuki
JNC TN8400 2000-016, 188 Pages, 2000/03
We summarized the conditions and results of all dissolution experiments (bench scale experiments (dissolution of sheared fuel pins) and beaker scale experiments (dissolution of a few sheared fuels pieces) of the irradiated fast reactor fuels, which were carried out in the Chemical Processing Facility (CPF). The fabrication and irradiation conditions of the dissolved fuels were also put in order.
; Koyama, Tomozo; Funasaka, Hideyuki
JNC TN8400 2000-014, 78 Pages, 2000/03
We investigated the factors which affected the dissolution of U and Pu to the nitric acid solution with the fragmentation model, which was based on the results of dissolution experiments for the irradiated fast reactor fuels in the Chemical Processing Facility(CPF). The equation that gave the fuel dissolution rate was estimated with the condition of fabrication (Pu ratio (Pu/(U+Pu))), irradiation (burn-up) and dissolution (nitric acid concentration, solution temperature and U+Pu concentration) by evaluating these effects quantitatively. We also investigated the effects of fuel volume ratio to the solution in the dissolver, burn-up and flouring ratio of the fuel on the f-value (the parameter which shows the diffusion and osmosis of nitric acid to the fuel) in the fragmentation model. It was confirmed that the fuel dissolution rate calculated with this equation had better agreement with the results of dissolution experiments for the irradiated fast reactor fuels in the CPF than that estimated with the surface area model. In addition, the efficiency of this equation was recognized for the dissolution of unirradiated U pellet and high Pu enriched MOX fuel. It was shown that the dissolution rate of the fuel slowed down at the condition of the high U-Pu concentration dissolution by the calculation of the dissolution behavior with this equation. The dissolution of the fuel can be improved by increasing the nitric acid concentration and temperature, but from the viewpoint of lowering the corrosion of the dissolver materials, it is desirable that the f-value is increased by optimizing the condition of shearing and stirring for the improvement of dissolution.
Moriyama, Hirotake*
JNC TJ8400 2000-050, 47 Pages, 2000/03
In support of the safety assessment of geologic disposal of high levcl radioactive wastes, the solubility of transuranium elements was studied. The solubility of PuO
 xH
xH O was measured undcr a reducing condition, and the solubility product K
O was measured undcr a reducing condition, and the solubility product K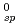 and the stability constant
and the stability constant 
 of Pu(OH)
of Pu(OH) were obtained. The obtained K
were obtained. The obtained K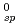 value was found to be much smaller than that predicted by Rai et al. from its dependence on ionic radius. Also, the solubility of PuO
value was found to be much smaller than that predicted by Rai et al. from its dependence on ionic radius. Also, the solubility of PuO 3
3  xH
xH O was measured under an oxidizing condition and the solubility product K
O was measured under an oxidizing condition and the solubility product K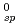 was obtained. In the analysis of hydrolysis constants of actinide ions, it was found that the systematic trend of the hydrolysis constants was well explained by the hard sphere model considering the effective charges of actinide ions.
was obtained. In the analysis of hydrolysis constants of actinide ions, it was found that the systematic trend of the hydrolysis constants was well explained by the hard sphere model considering the effective charges of actinide ions.
Ueta, Shinzo*; *; *; *
JNC TJ8400 2000-002, 364 Pages, 2000/02
Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) have been setting migration parameters and developing its database for the 2nd Progress Report of HLW Geological Disposal (H12 Report). In this study, experimentswere carried out to certify the reliability of parameters and scenario, and examination was carried out to survey procedures of quality management. The main contents are as follows. (1)Data acquisition for certification of migration parameters. The effect of NH complex of Pd on distribution coefficients (Kd) of Pd on both bentonite and rocks, and the effect of sulfate and carbonate complexes of Am on Kds of Am on bentonite are investigated. Kds of Pd depended on NH
complex of Pd on distribution coefficients (Kd) of Pd on both bentonite and rocks, and the effect of sulfate and carbonate complexes of Am on Kds of Am on bentonite are investigated. Kds of Pd depended on NH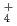 concentration in aqueous. The dependence varied with pH. Effects of sulfate and carbonate complexes on Kds of Am were not remarkable. Apparent diffusivities of Cs in bentonite saturated by saline water were measured. It was confirmed that the apparent diffusivities of Cs in saline water were similar to those in pure water. (2)Evaluation of colloidal effect on nuclide migration. An evaluation of validity of analytical model (Hwang's model) for nuclide migration under existence of colloids and investigation of characterization of colloids in groundwater were carried out. As the results, it was indicated that the Hwang's model was appropriate, and it was found that samplingtechnique influenced concentration and size distribution of colloids. (3)Influence of organic substances on solubility. Solubility of Th was measured under the condition with humic acid and carbonate. It increased roughly in proportion to the concentration of humic acid. And it was remarkably high under the condition with carbonate. It was confirmed that Th solubility data set in H12 report was conservative, even though humic acid existed in groundwater. (4)Use of Mechanistic Models for Safety Assessment. The integrated sorption/diffusion model has been used to calculate K
concentration in aqueous. The dependence varied with pH. Effects of sulfate and carbonate complexes on Kds of Am were not remarkable. Apparent diffusivities of Cs in bentonite saturated by saline water were measured. It was confirmed that the apparent diffusivities of Cs in saline water were similar to those in pure water. (2)Evaluation of colloidal effect on nuclide migration. An evaluation of validity of analytical model (Hwang's model) for nuclide migration under existence of colloids and investigation of characterization of colloids in groundwater were carried out. As the results, it was indicated that the Hwang's model was appropriate, and it was found that samplingtechnique influenced concentration and size distribution of colloids. (3)Influence of organic substances on solubility. Solubility of Th was measured under the condition with humic acid and carbonate. It increased roughly in proportion to the concentration of humic acid. And it was remarkably high under the condition with carbonate. It was confirmed that Th solubility data set in H12 report was conservative, even though humic acid existed in groundwater. (4)Use of Mechanistic Models for Safety Assessment. The integrated sorption/diffusion model has been used to calculate K , D
, D and D
and D values ...
values ...
Sakamura, Y.*; Shirai, Osamu; Iwai, Takashi; Suzuki, Yasufumi
Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 147(2), p.642 - 649, 2000/02
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:61.09(Electrochemistry)no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji
Genankyo Dayori, (173), p.11 - 14, 2000/01
no abstracts in English
; Makino, Hitoshi; Peter*
JNC TN8400 99-095, 69 Pages, 1999/12
MESHNOTE code was developed to evaluate the engineered barrier system in collaboration with QuantiSci. This code is used to simulate glass dissolution, diffusive transport of nuclides in the buffer material and release to surrounding host rock. MESHNOTE is a one-dimensional finite difference, code, which uses cylindrical co-ordinates for the solution of a radially symmetric diffusion problem. MESHNOTE has the followig characteristics: (1) MESHNOTE can solve for diffusive transport of nuclides through an annulus shaped buffer region while accounting for multiple decay chains, linear and non-linear sorption onto the buffer materials and elemental solubility limits; (2) MESHNOTE can solve for ingrowth of plural daughter nuclides from a singular parent nuclide (branching), and the ingrowth of a singular daughter nuclide from plural parent nuclides (rejoining); (3) MESHNOTE can treat the leaching of nuclide from the vitrified waste and the release of nuclide from buffer to surrounding rock, which are boundary conditions for migration in the buffer, basing on the phenomena; (4) MESHNOTE can treat principal parameters (e.g. solubility and distribution coefficient) relevant to nuclide migration as time and space-dependence parameters; (5) The time stepping scheme in MESHNOTE is controlled by tolerance defined by the user. The time stepping will increase automatically while checking the accuracy of the numerical solution. The conceptual model, the mathematical model and the numerical implementation of the MESHNOTE code are described in this report and the characteristic functions of MESHNOTE are verified by comparing with analytical solutions or simulations produced with other calculation codes.
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu, 6(1), p.147 - 149, 1999/12
no abstracts in English